
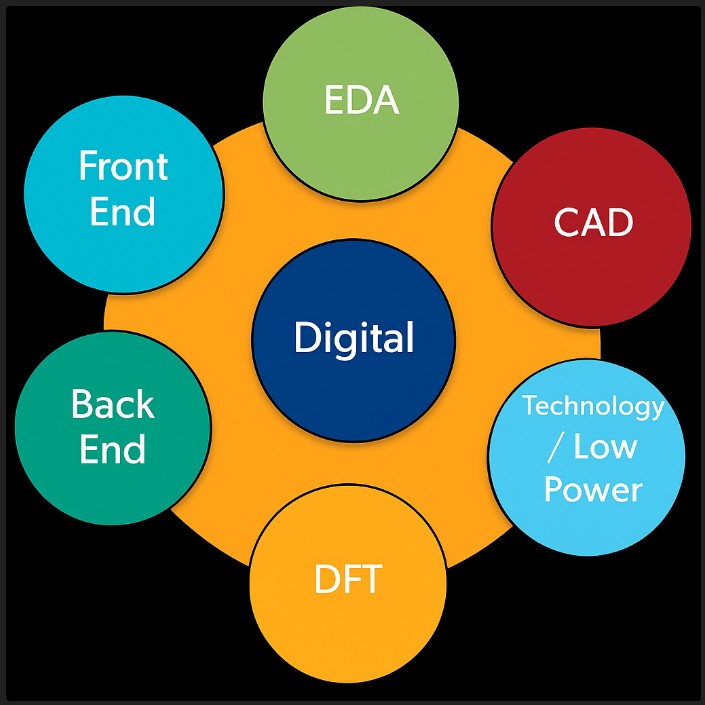
When we talk about VLSI careers, one of the most attractive and in-demand areas is ASIC Digital Jobs. Whether you are an undergraduate, a master’s student, or an experienced professional in Electronics and Communication (EC) or Electrical Engineering (EEE), understanding these roles can help you shape a rewarding path in the semiconductor industry.
This session is designed to simplify complex job profiles. As an industry expert, I’ll explain how each digital ASIC role contributes to chip design and why it is critical in today’s semiconductor and microelectronics ecosystem.
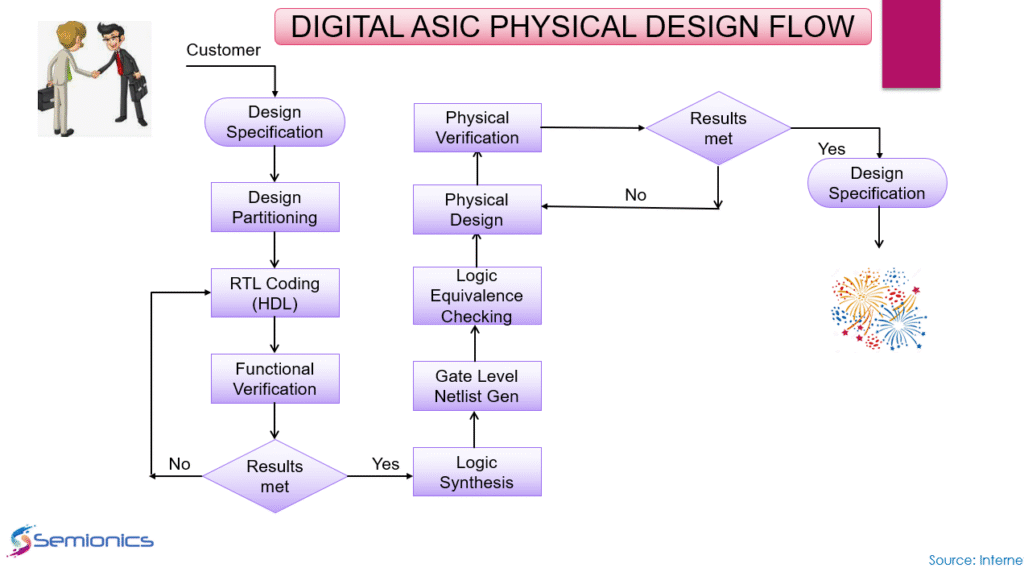
RTL Design and Verification
Engineers write hardware description code and test it to ensure correct functionality. It forms the foundation of digital ASIC development.
Design Implementation
This role focuses on converting RTL into gate-level design using synthesis tools. Accuracy and optimization are the primary goals.
Physical Design
Engineers work on placement, clock tree synthesis, and routing of circuits. It ensures the design fits into silicon effectively.
Static Timing Analysis (STA) / Timing
This involves verifying timing constraints and ensuring the chip meets performance requirements. STA engineers play a crucial role in closing timing issues.
Physical Verification and Extraction
These engineers check the layout for design rule violations and extract parasitics to ensure the chip works in real silicon.
CAD / Methodology
They develop automation scripts and flows to simplify design processes. This role is vital for efficiency in large-scale projects.
Low Power Design
Engineers work on power optimization techniques like clock gating and power gating. Low-power experts are in high demand for mobile and IoT applications.
Design for Testability (DFT)
DFT engineers insert test structures to validate chips post-fabrication. It helps reduce defective parts and enhances product reliability. EDA Related Roles
Every role in digital ASIC VLSI jobs is interconnected. RTL engineers rely on verification experts, while physical design teams collaborate with STA and verification engineers. This ecosystem ensures high-performance, low-power, and reliable semiconductor chips reach the market.
For fresh graduates and professionals, the first step is to identify your strength—whether in coding, debugging, circuit optimization, or automation. Then, align your career with the right specialization.
At Semionics, we guide aspiring engineers and professionals in mastering these skills. With specialized training programs in VLSI design, verification, and physical design, you gain both technical depth and industry-level exposure.
To Upskill yourself , you can access the whole Session for Free by clicking the link below

https://academy.semionics.com/courses/Defining-Analog-ASIC-VLSI-Jobs-658e6047e4b0d4e41c3a2a2c
At Semionics, we provide hands-on training, industry exposure, and mentorship for engineers aspiring to enter analog VLSI jobs. Our programs cover design, layout, EDA methodologies, and verification.
The images and content used in this blog are generated, created, or referenced from Google Images and other educational sources. They are intended purely for educational and guidance purposes, with no intention of monetization. All credits belong to the respective owners. Semionics holds no responsibility for third-party content and encourages readers to verify before use.